Oil degumming is a key step in the oil refining process, the purpose of which is to remove the colloid impurities (such as phospholipids, proteins, mucus, etc.) in the oil. These impurities may cause the oil to oxidize and deteriorate during storage and use, affecting its quality and taste. Degumming is usually the first step in vegetable oil refining, especially in edible oil production.
Main methods of oil degumming:
Hydration degumming:
Principle: Lecithin and other colloids will form micelles or precipitates when they come into contact with water, so they can be separated.
Steps: Add an appropriate amount of water or steam to the oil to swell and precipitate the colloids in the oil. Then separate the colloids and oils by a centrifuge.
Scope of application: Mainly used for oils with more phospholipids, such as soybean oil, peanut oil, etc.
Acid degumming:
Principle: By adding acid (such as phosphoric acid or citric acid), phospholipids undergo chemical reactions to form oil-insoluble precipitates, which are then separated by centrifugation.
Advantages: It can remove some impurities that are difficult to remove by hydration degumming, such as non-hydratable phospholipids.
Scope of application: Suitable for high-quality refined oil production, commonly used in vegetable oil refining.
Enzymatic degumming:
Principle: Use specific enzymes (such as phospholipases) to hydrolyze phospholipids in the oil to decompose it into products that are easier to remove.
Advantages: Higher oil quality can be obtained with less oil loss.
Scope of application: High-end oil refining, especially the production of oils with high nutritional value, such as high-end edible oils.
Physical degumming (supercritical degumming, etc.):
Principle: Separate phospholipids and oils through physical means such as supercritical fluids or other high-tech methods.
Advantages: Advanced technology, can maintain the natural quality of oils, suitable for high value-added oils.
Disadvantages: Complex equipment and high investment cost.
Effect of degumming:
Improve oil stability: After removing the colloid, the oil is not easy to oxidize and precipitate during storage, which helps to extend the shelf life.
Improve oil quality: The oil after degumming has higher transparency, better color and better taste, suitable for food processing and direct consumption.
Reduce processing difficulty: When the degummed oil enters the subsequent refining process (such as deacidification, decolorization, and deodorization), it is more efficient and reduces losses.
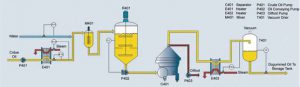
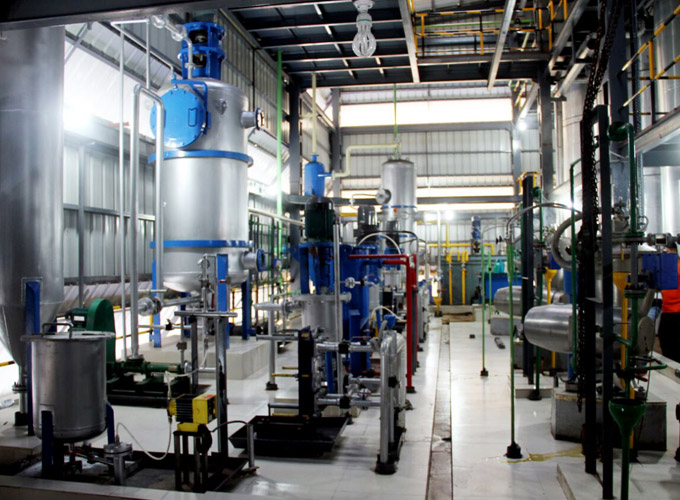
Oil degumming equipment is an important equipment used to remove colloidal impurities in oil in the refining process. With the development of oil refining technology, the types and technical levels of degumming equipment have also been continuously improved to meet the production needs of different scales and types of oil. The following are the main types of oil degumming equipment and their working principles:
1. Hydration degumming equipment
Working principle: Hydration degumming equipment adds water or steam to crude oil to make colloidal impurities (mainly phospholipids) absorb water and swell to form separable precipitates, and then separates these impurities from the oil through a centrifuge or sedimentation tank.
Equipment composition:
Mixing tank: used to fully mix oil with water or steam to ensure that the colloidal impurities are fully hydrated.
Heater: used to adjust the temperature of oil to make the degumming effect better.
Centrifuge: separate the hydrated colloidal impurities from the oil.
Sedimentation tank: used to settle and separate some larger colloidal impurities.
2. Acid degumming equipment
Working principle: Acid degumming is done by adding a certain amount of phosphoric acid or citric acid to the oil to make the phospholipids in the oil react chemically to form separable precipitates. These precipitates are usually separated by a centrifuge.
Equipment composition:
Acid reactor: used for the full mixing of oil and acid to convert phospholipids into precipitates.
Heater: controls the temperature to promote the acidification reaction.
Centrifuge: separates the precipitates generated by acidification.
3. Enzymatic degumming equipment
Working principle: Enzymatic degumming equipment uses enzymes (such as phospholipases) to catalyze the decomposition reaction of phospholipids to generate easily separable products. Compared with traditional hydration or acid degumming, enzymatic degumming can more effectively remove non-hydratable phospholipids and maintain the high nutritional value of oil.
Equipment composition:
Enzyme reaction tank: used for the full reaction of oil and enzyme, controlling temperature and time.
Mixing system: ensures that the enzyme and oil are evenly mixed.
Filter or centrifuge: used to separate impurities and oil produced after the reaction.
4. Supercritical degumming equipment
Working principle: Supercritical degumming uses supercritical fluids (such as supercritical carbon dioxide) to separate colloids from oils and fats. The characteristics of supercritical fluids can effectively remove colloid impurities in oils and fats without damaging the nutritional content and natural quality of oils and fats.
Equipment composition:
Supercritical reactor: Keep the fluid in a supercritical state by controlling temperature and pressure.
Separation system: Separate colloids from oils and fats and collect the purified oils and fats.
Pressure control system: Precisely control the pressure conditions during the reaction process.
5. Automated degumming equipment
Features: Modern oil and fat processing plants are increasingly using automated degumming equipment, which is equipped with automatic control systems that can automatically adjust the amount of additives such as water, acid, enzymes, temperature, pressure and other parameters according to production needs to ensure the efficiency and stability of the degumming process.
Equipment composition:
PLC control system: Realize precise automatic control and monitoring.
Online sensor: Real-time monitoring of oil quality parameters such as phospholipid content and temperature.
Automatic mixing system: Automatically add water, acid or enzyme according to the set process parameters to ensure the consistency and efficiency of oil and fat processing.
6. Centrifugal degumming machine
Working principle: Centrifugal degumming equipment uses centrifugal force to separate impurities from oil and fat, and is often used in hydration degumming and acidification degumming processes. Through high-speed rotation, heavier impurities (such as phospholipids) are deposited on the separator wall, and lighter oil and fat are collected in the center.
Equipment composition:
High-speed centrifuge: to achieve fast and effective separation of oil and impurities.
Oil collection system: to collect pure oil after centrifugal separation.
Sediment discharge system: to automatically discharge the separated colloidal sediment.
Key points for equipment selection:
Oil type: Different oils (such as soybean oil, peanut oil, palm oil, etc.) contain different types and quantities of colloidal impurities, and the required degumming equipment will also be different.
Production scale: large-scale production requires highly automated degumming equipment, while small-scale production can choose simpler equipment.
Degumming process: according to the production target (such as high-quality refined oil or ordinary edible oil), select the equipment required for different processes such as hydration, acidification, and enzyme method.
Oil degumming equipment is the core equipment in oil refining. Its selection and use directly affect the quality, stability and production efficiency of oil.
